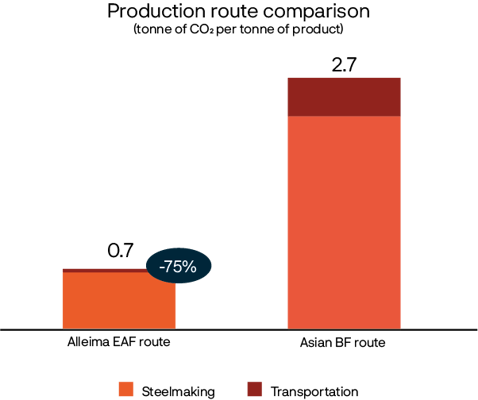
One of the key advantages of LCA is that it pinpoints the areas within a product’s lifecycle with the most significant environmental impact. With this information at hand, we can then specifically target areas for improvement, effectively reducing the product’s carbon footprint. By analyzing resource usage, for example, it is also possible to optimize the utilization of resources, such as switching to materials with lower carbon footprints.
1. Identifying hotspots
Identifying environmental hotspots within a product’s lifecycle provides valuable insight on where the greatest impacts occur, such as during material production, energy use, transportation or end-of-life. With this insight, improvement efforts can be directed toward the stages that contribute most to the overall product carbon footprint, enabling more effective and measurable climate reductions.
2. Resource preservation
By mapping how materials and energy are consumed throughout the lifecycle, an LCA can reveal opportunities to optimize resource use. This may involve reducing waste, improving process efficiency, or selecting alternative materials with lower climate impact. Such optimizations support long-term resource preservation and help strengthen environmental performance.
3. Costs savings
Many of the efficiency opportunities identified through LCA can also lead to potential cost savings. More efficient processes tend to consume fewer resources, require less energy, and generate less waste, all of which contribute to reduced operational expenditures.
4. Competetive advantages
Transparent and reliable environmental data enhance credibility with customers and other stakeholders. Companies that can demonstrate verified climate performance gain a competitive edge, especially as sustainability requirements become increasingly important in procurement. By providing clear insights into the environmental impact of products, LCA contributes to stronger customer relationships and supports stakeholders in reaching their climate targets.