Alleima® 5R10 is an austenitic chromium-nickel steel with a controlled carbon content in order to obtain improved strength at high temperatures.
Standards
- ASTM: TP304, TP304H
- UNS: S30400, S30409
- EN Number: 1.4301, 1.4948
- EN Name: X5CrNi18-10, X6CrNi18-10
- W.Nr.: 1.4301
- DIN: X 5 CrNi 18 10
- SS: 2333
- AFNOR: Z 6 CN 18.09
- BS: 304S31, 304S51
- JIS: SUS304TP
Product standards
Seamless tube and pipe
- ASTM A271 and A376
- JIS G3459
- JIS G3463
- EN 10216-5
- BS 3605, BS 3606
- DIN 17456, 17458
- NFA 49-117, 49-217
- SS 14 23 33
Approval
JIS Approval for Stainless Steel Tubes
Chemical composition (nominal)
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.04 | 0.4 | 1.3 | ≤0.040 | ≤0.015 | 18.5 | 9.5 |
Subject to agreement, material with extra low Co content can be supplied.
Applications
Alleima® 5R10 is used for a wide range of industrial applications with emphasis on high temperature processes. Typical examples are: heat exchangers, condensers, pipelines, cooling and heating coils in the chemical, petrochemical, fertilizer, pulp and paper and nuclear power industries, as well as in the production of pharmaceuticals, foods and beverages.
Corrosion resistance
General corrosion
Alleima® 5R10 has good resistance in:
- Organic acids at moderate temperatures
- Salt solutions, e.g. sulfates, sulfides and sulfites.
- Caustic solutions at moderate temperatures
The risk of general corrosion in sulfuric acid during shut down periods has to be taken into account. Since Alleima® 5R10 is not alloyed with molybdenum, the grade can only tolerate low concentrations at limited temperatures. In naturally aerated sulfuric acid the corrosion rate is below 0.1 mm/year provided the temperature is not higher than 20°C (68oF) in 5% solution.
Intergranular corrosion
Alleima® 5R10 has a relatively high carbon content. Thus, there is a certain risk of reduced intergranular corrosion resistance if the steel has become sensitized after e.g. improper heat treatment or welding. Alleima® 3R12 has a significantly lower carbon content and is therefore more safe regarding intergranular attack.
Pitting and crevice corrosion
The steel may be sensitive to pitting and crevice corrosion even in solutions of relatively low chloride content. Molybdenum alloyed steels have better resistance and the resistance improves with increasing molybdenum content.
Stress corrosion cracking
Austenitic steel is susceptible to stress corrosion cracking. This may occur at temperatures above about 60°C (140°F) if the steel is subjected to tensile stresses and at the same time comes into contact with certain solutions, particularly those containing chlorides. Such service conditions should therefore be avoided. Conditions when plants are shut down must also be considered, as the condensates which are then formed can develop conditions that lead to both stress corrosion cracking and pitting.
In applications demanding high resistance to stress corrosion cracking we recommend the austenitic-ferritic steel SAF™ 2304.
Gas corrosion
Alleima® 5R10 can be use in
- Air up to 850°C (1560°F)
- Steam up to 750°C (1380°F)
- Synthesis gas (ammonia synthesis) up to about 550°C (1020°F)
Creep behavior should also be taken into account when using the steel in the creep range. In flue gases containing sulfur, the corrosion resistance is reduced. In such environments the steel can be used at temperatures up to 600-750°C (1110-1380°F) depending on service conditions.
Factors to consider are whether the atmosphere is oxidizing or reducing, i.e. the oxygen content, and whether impurities such as sodium and vanadium are present.
Bending
Annealing after cold bending is not normally necessary, but this point must be decided with regard to the degree of bending and the operating conditions. Heat treatment, if any, should take the form of stress relieving or solution annealing, see under "Heat treatment".
Hot bending is carried out at 1100-850°C (2010-1560°F) and should be followed by solution annealing.
Forms of supply
Seamless tube and pipe
Tube and pipe are normally delivered in the solution annealed and white-pickled condition or in the bright-annealed condition. The size range can be seen from Fig. 1. U-tubes can be delivered on request.
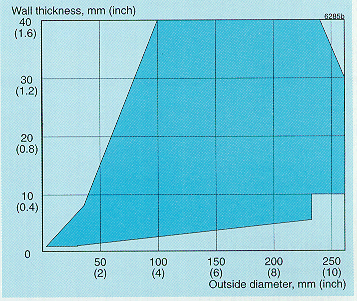 Figure 1. Principal size range for seamless tube and pipe.
Figure 1. Principal size range for seamless tube and pipe.
Heat treatment
The tubes are normally delivered in heat treated condition. If additional heat treatment is needed after further processing the following is recommended.
Stress relieving
850-950°C (1560-1740°F), cooling in air.
Solution annealing
1000-1100°C(1830-2010°F), rapid cooling in air or water.
Mechanical properties
For tube and pipe with wall thickness greater than 10 mm (0.4 in.) the proof strength may fall short of the stated values by about 10 MPa (1.4 ksi)
At 20°C (68°F)
| Proof strength | Tensile strength | Elong. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rp0.2a) | Rp1.0a) | Rm | Ab) | A2" | |||
| MPa | ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | ksi | % | % |
| ≥210 | ≥30 | ≥240 | ≥35 | 515-690 | 75-100 | ≥45 | ≥35 |
1 MPa = 1 N/mm2
a) Rp0.2 and Rp1.0 corresponds to 0.2% offset and 1.0% offset yield strength, respectively.
b) Based on L0 = 5.65 √S0 where L0 is the original gauge length and S0 the original cross-section area.
The hardness (Vickers) is approximately 155
Impact strength
Due to its austenitic microstructure, Alleima 5R10 has very good impact strength both at room temperature and at cryogenic temperatures.
Tests have demonstrated that the steel fulfils the requirements (60 J (44 ft-lb) at -196 oC (-320 oF)) according to the European standards EN 13445-2 (UFPV-2) and EN 10216-5.
At high temperatures
|
Temperature
|
Proof strength
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Rp0.2 | Rp1.0 | |
| °C | MPa | MPa |
| min | min | |
| 50 | 190 | 215 |
| 100 | 165 | 190 |
| 150 | 150 | 175 |
| 200 | 140 | 165 |
| 250 | 130 | 155 |
| 300 | 125 | 150 |
| 350 | 120 | 145 |
| 400 | 115 | 140 |
| 450 | 110 | 135 |
| 500 | 105 | 130 |
| 550 | 100 | 125 |
| 600 | 95 | 120 |
|
Temperature
|
Proof strength
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Rp0.2 | Rp1.0 | |
| °F | ksi | ksi |
| min | min | |
| 200 | 24 | 28 |
| 400 | 20 | 24 |
| 600 | 18 | 22 |
| 800 | 16 | 20 |
| 1000 | 15 | 18 |
| Temperature | 10 000 h | 100 000 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | °F | MPa | ksi | MPa | ksi |
| approx. | approx. | approx. | approx. | ||
| 550 | 1020 | 195 | 28.3 | 115 | 16.6 |
| 575 | 1065 | 147 | 21.3 | 93 | 13.5 |
| 600 | 1110 | 122 | 17.6 | 74 | 10.7 |
| 625 | 1155 | 100 | 14.5 | 58 | 8.4 |
| 650 | 1200 | 79 | 11.5 | 45 | 6.5 |
| 675 | 1245 | 64 | 9.2 | 33 | 4.8 |
| 700 | 1290 | 48 | 7.0 | 23 | 3.3 |
Physical properties
Density: 7.9 g/cm3, 0.29 lb/in3
| Temperature, °C | W/m °C | Temperature, °F | Btu/ft h °F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 14 | 68 | 8 |
| 100 | 15 | 200 | 8.5 |
| 200 | 17 | 400 | 10 |
| 300 | 18 | 600 | 10.5 |
| 400 | 20 | 800 | 11.5 |
| 500 | 21 | 1000 | 12.5 |
| 600 | 23 | 1100 | 13 |
| Temperature, °C | J/kg °C | Temperature, °F | Btu/lb °F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 485 | 68 | 0.11 |
| 100 | 500 | 200 | 0.12 |
| 200 | 515 | 400 | 0.12 |
| 300 | 525 | 600 | 0.13 |
| 400 | 540 | 800 | 0.13 |
| 500 | 555 | 1000 | 0.13 |
| 600 | 575 | 1100 | 0.14 |
| Temperature, °C | Per °C | Temperature, °F | Per °F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30-100 | 16.5 | 86-200 | 9.5 |
| 30-200 | 17 | 86-400 | 9.5 |
| 30-300 | 17.5 | 86-600 | 10 |
| 30-400 | 18 | 86-800 | 10 |
| 30-500 | 18.5 | 86-1000 | 10 |
| 30-600 | 18.5 | 86-1200 | 10.5 |
| 30-700 | 19 | 86-1400 | 10.5 |
1) Mean values in temperature ranges (x10-6)
| Temperature, °C | MPa | Temperature, °F | ksi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 200 | 68 | 29.0 |
| 100 | 194 | 200 | 28.2 |
| 200 | 186 | 400 | 26.9 |
| 300 | 179 | 600 | 25.8 |
| 400 | 172 | 800 | 24.7 |
| 500 | 165 | 1000 | 23.5 |
1) (x103)
Welding
The weldability of Alleima® 5R10 is good. Welding must be carried out without preheating and subsequent heat treatment is normally not required. Suitable methods of fusion welding are manual metal-arc welding (MMA/SMAW) and gas-shielded arc welding, with the TIG/GTAW method as first choice.
For Alleima® 5R10, heat input of <1.5 kJ/mm and interpass temperature of <150°C (300°F) are recommended.
Recommended filler metals
TIG/GTAW or MIG/GMAW welding
ISO 14343 S 19 9 H / AWS A5.9 ER308H
MMA/SMAW welding
ISO 3581 E 19 9 H R / AWS A5.4 E308H-17
Disclaimer: Recommendations are for guidance only, and the suitability of a material for a specific application can be confirmed only when we know the actual service conditions. Continuous development may necessitate changes in technical data without notice. This datasheet is only valid for Alleima materials.