Revolutionizing iron ore heating with HYBRIT
The Swedish target of zero emissions by 2045 has challenged the steel industry. HYBRIT, which stands for “hydrogen breakthrough ironmaking technology,” is a joint venture between the steel company SSAB, the mining company LKAB and the power company Vattenfall.
The aim of HYBRIT is to revolutionize steelmaking technology by replacing the coal-based blast furnace process with a direct reduction process based on hydrogen. The result will be a fossil-free value chain, from mine to steel. One of the challenges in the HYBRIT process is the ability to preheat large amounts of hydrogen.
“To succeed, the project requires an efficient and fossil-free process to heat the hydrogen, and this is where we enter the picture,” says Dilip Chandrasekaran, Head of Research and Development at Allemia division Kanthal, a world leader in the area of industrial heating technology and resistance materials.
Says SSAB CEO Martin Lindqvist, “When we started HYBRIT five years ago, a lot of people didn’t believe in the idea, which requires that you replace a production method that has worked for a thousand years. Now we have proved that it’s possible.”
HYBRIT currently operates a pilot plant in northern Sweden, where the first Kanthal heater is ready for testing. The heater is in the 250 kilowatt range, and if it proves successful it will be upgraded to a 1 megawatt version. The goal is to develop a large-scale heating solution that could heat high volumes of hydrogen up to 1,000°C (1,832°F).
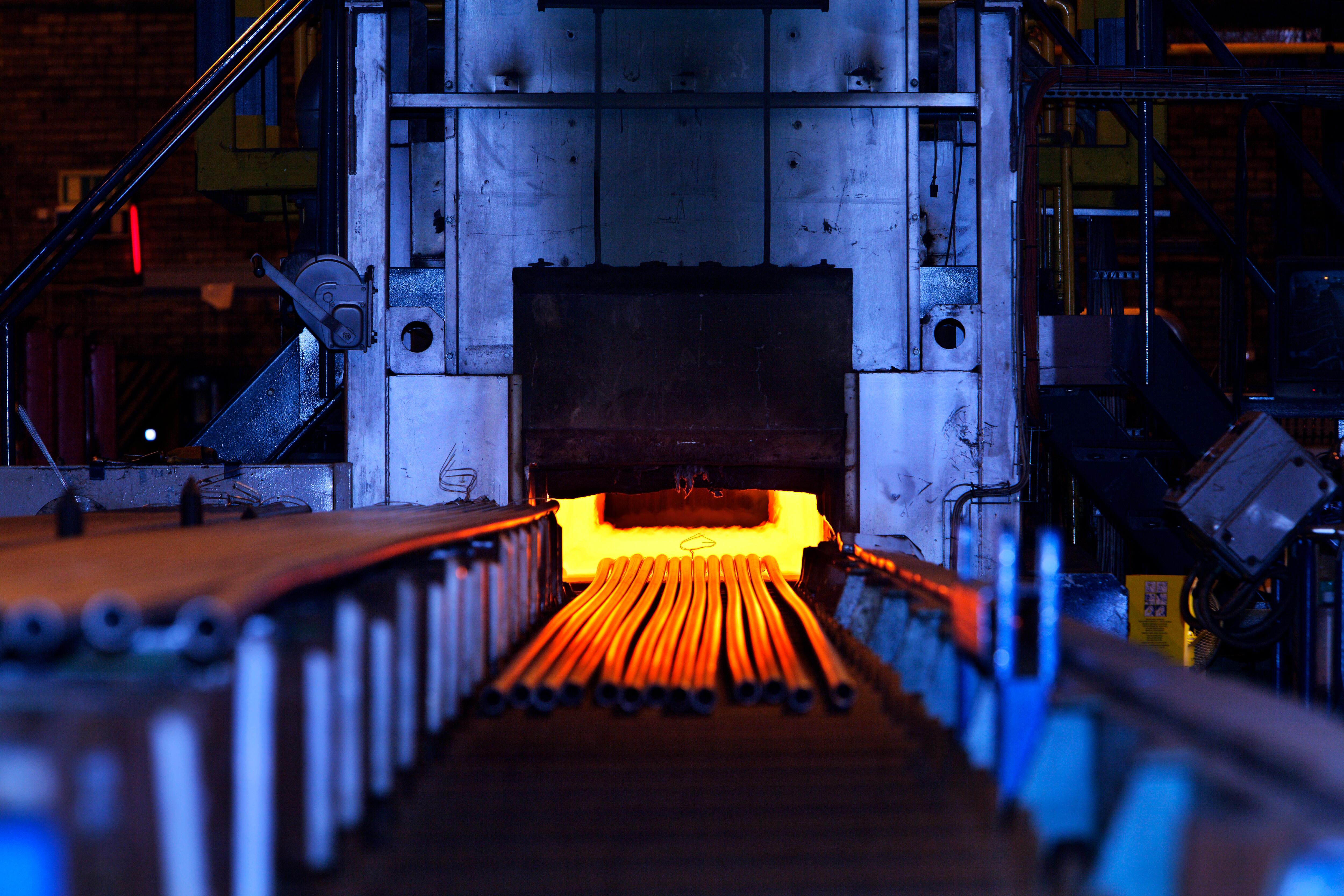

“This is groundbreaking for Alleima and Kanthal, and also for HYBRIT,” says Anders Björklund, President of Kanthal. “It is a huge leap from kilowatts to megawatts and is something that has never been done before. It is one thing to have a technical solution, but it is quite another to have a solution that is robust and reliable enough to operate in the steel industry.”
Read more: Kanthal supports HYBRIT in quest to develop world’s first fossil free sponge iron — Kanthal®
Compressor revolution – cool solutions for a hotter world
Cooling down is catching on. As incomes rise and populations grow, especially in the world’s hotter regions, the use of air conditioners is becoming increasingly common. In fact, the use of air conditioners and electric fans already accounts for about one-fifth of total electricity consumption in buildings around the world – or 10 percent of all global electricity consumption.
Over the coming three decades, the use of AC is set to soar, becoming one of the top drivers of global electricity demand. A new analysis by the International Energy Agency shows how new standards can help the world avoid facing the predicted “cold crunch” by helping improve efficiency while also staying cool.

Global energy demand from air conditioners is expected to triple by 2050. The International Energy Agency stresses the urgent need for policy action to improve cooling efficiency. Compressors used in ACs, as well as refrigerators, are crucial to their energy efficiency as well as to reducing the noise level and size of the appliances.
Alleima Hiflex compressor valve steel has already brought significant benefits to major manufacturers of refrigerator compressors. The key to reducing energy consumption and increasing cooling capacity is a higher lift of the “tongue” of the compressor valve, which exposes it to much higher fatigue loads. Only Hiflex can meet the mechanical property requirements for bending and thus impact fatigue strength.
Read more: The Future of Cooling – Analysis - IEA
Fuel cell frenzy
The global fuel cell market is projected to grow from USD 3.36 billion in 2021 to USD 28.95 billion in 2028 at a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 36.0 percent during the period (Source: Fortune Business Insight). Alleima produces coated strip steel for fuel cell bipolar plates with advanced production and coating technology that makes the fuel cell plates more durable and efficient compared with other methods of production. Our unique large-scale production plant for coated strip steel can also reduce costs for fuel cell manufacturers.
The development of fuel cells is accelerating worldwide, moving from laboratory-scale and prototype programs to industrial-scale production, which poses another challenge for manufacturers. As an example, a single hydrogen-powered automobile or bus has between 500 and 600 bipolar plates in a single fuel cell stack. So if only 1 percent of all cars produced in the world were hydrogen-powered, that would require the production of hundreds of millions of bipolar plates each year.

Given all the potential applications for hydrogen fuel cells, mass production will be an absolute necessity. However, current attitudes toward the mass production of fuel cells can be summed up by the opinion of Herbert Diess, CEO of Volkswagen Group, who points out that the technology, in general, is “expensive … and difficult to roll out.”
But there are ways of making the production of bipolar plates less costly and more efficient. A common method of producing bipolar plates is stamping uncoated stainless steel, laser-cut, welding and coating one plate at a time This value chain will be challenged in terms of capacity as it is time-consuming, even with a high automation level. The Alleima continuous roll-to-roll PVD coating process is efficient and suitable for big volumes. The precoated strip can be fed directly into the customer stamping tools, producing thousands of bipolar plates from each coil. The coating is based on environmentally friendly coating technology that produces bipolar plates made out of 100 percent recyclable material, with no discharge to water or air and no toxic residues.
Processes such as the Alleima SurfTech Smarter Coatings concept will be essential for making hydrogen fuel cells commercially viable over the coming years.
Read More at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/fuel-cell-market-100733
Life-changing science
Diabetes, coronary and cardiovascular diseases, Parkinson’s and impaired hearing are some of the unwanted consequences of longer lifespans. Diabetes is one of the major causes of death in the world. Currently some 422 million individuals are affected. To them, continuous measuring of glucose levels is essential to maintain good health.
Medtech innovation helps increase the quality of life for those afflicted, prolonging and sometimes saving lives in the process. Alleima offers a comprehensive range of high-grade fine wires and wire-based components for applications in various fields of medical technology, including glucose meters, hearing implants, in-brain neurostimulation for Parkinson’s sufferers and vascular cleansing treatment.
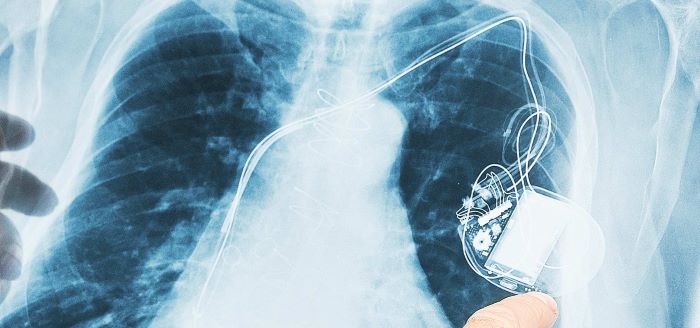
Neurostimulation is a wide branch of therapeutic activation and stimulation of the nervous system such as brain stimulation, deep brain stimulation, spinal cord stimulation and others. Neurostimulation is generally based on the utilization of electrical impulses transmitted to the part of the nervous system that is functioning improperly.
At our U.S. production facility in Palm Coast, Florida, Alleima makes wire-based components used for medical devices that are in many cases life-saving, but most of all life-changing, such as those related to diabetes, heart conditions and hearing loss – devices that can return you to an almost normal life, or as one user put it “a new normal life.”
Read more: Exera fine medical wire — Alleima
Fertilizers help feed the world
The demand for fertilizer, especially in the agriculture sector has increased rapidly as a growing population has led to an increase in the demand for food. In addition, the lack of nutrients in the soil due to the use of pesticides and other harmful chemicals has led to a decline in agricultural productivity. This is expected to increase the demand for fertilizers. The global fertilizer market size is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.2 percent from 2020 to 2026. The growing demand for food will largely intensify the fertilizer demand for better crop production in restricted arable lands.
Increasing demands for food from less arable land to support expanding populations in the Asia Pacific means the fertilizer market in the region is set for particularly strong growth. The region’s fertilizer market was valued at USD 9.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to register a CAGR of almost 7 percent over the next five years.

At the same time, players in the fertilizer industry are continually seeking ways to improve efficiency and productivity while simultaneously reducing maintenance costs and unscheduled downtime.
Urea is a critical component of common fertilizers, and its production occurs in extremely corrosive, high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Using high-quality materials from Alleima that can withstand these conditions delivers tangible benefits for plant operators.