We produce martensitic stainless chromium knife steels. These steels become stainless only after correct hardening, when carbides have been dissolved.
There are also many other types of stainless steels, but these are different in composition and structure and are rarely used in edge applications, since the edge properties are inferior to those of martensitic stainless steel grades.
Differences between carbon steel and stainless steel
There are two main differences between carbon knife steel and stainless knife steel. The first is that stainless steels have much higher corrosion resistance, due to the protective chromium oxide layer that covers the steel surface after heat treatment. The second difference relates to the alloying elements that form carbides. Stainless steels contain at least 10.5% by weight of chromium. The carbide particles provide the steel with significant wear resistance. The carbides are bonded together by the steel matrix.
The importance of carbide size
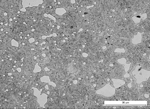
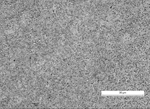
A knife steel with large carbides is generally very difficult to regrind, since the carbides crumble out of the edge and cause a 'saw edge' instead of a razor-sharp edge. We produce knife steels with fine carbides which enable excellent edge sharpness. The pictures below show the microstructures of the three classes of stainless steel on the market.
Coarse-carbide tool steel grades
Fine-carbide knife steels
Combination of knife steel properties
The table shows combinations of knife steel properties for different classes of steel. Note that corrosion is detrimental for the cutting edge. Consequently the lack of sufficient corrosion resistance also affects knife performance and not only the esthetics of the blade.
| Edge performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel type | Sharpness | Edge stability | Wear resistance | Toughness | Corrosion resistance |
| Coarse- carbide steels1) |
Poor
|
Poor
|
Excellent
|
Poor
|
Very good
|
| Fine-carbide knife steels2) |
Excellent
|
Excellent
|
Very good
|
Excellent
|
Very good
|
| Carbon steels3) |
Excellent
|
Excellent
|
Poor
|
Excellent
|
Insignificant
|
Material examples:
1) ASTM 440A, 440C, D2; 9Cr18MoV; 19C27
2) 14C28N, 13C26, 12C27, 12C27M, 7C27Mo2
3) ASTM 1095, 1075